[guide] branch jump line is a fiber optic cable component, one end is a multi core MTP joint, the other end is a branch with a single core or double core LC connector with an outer sheath. It provides a conversion for the backbone cable of the MTP joint, the trunk extension cable or the back of the single core / double core connector module. Figure 1 shows some examples of different composition of the branch jumpers.
This paper will be used as the best guide for MTP LC branch jumpers to be applied in structured cabling applications. It will focus on 12 core and 8 core MTP to LC branch jumper cables, which are widely used in LAN and LC duplex optical ports from SAN vendors from different manufacturers.
What is the MTP-LC branch jump line?
The branch jumper is a fiber optic component with one end of a multi core MTP joint and a branch with an outer sheath with a single or double core LC connector. It provides a conversion for the backbone cable of the MTP joint, the trunk extension cable or the back of the single core / double core connector module. Figure 1 shows some examples of different composition of the branch jumpers.

What's the advantage of using the MTP-LC branch jumper?
When designing a network system, it is very important to plan a structured wiring in advance. Our goal is to solve the current network needs and adapt to the future development. Structured cabling systems can flexibly deal with the usual execution of mobile, increase or change the task of infrastructure, with the development of the network. Using a MTP-LC branch jumper to use a high density local area network or a storage switch can help you improve structured wiring.
The use of branch jumper components to compare some of the main advantages of traditional jumpers:
The 1. branch jumper provides a clean and high-density way to achieve high density switch port replication, which can reduce the risk of port damage or error.
The 2. branch jumper has less space in the cabinet and better vertical management than the traditional jumper. The branch of the 12 core jumper is much less than the one with the same core number.
3. reduce optical cable congestion for LAN and storage networks; it can improve the cooling air flow and make it easier to move, increase and change (MAC).
The 4. branch jumper can provide interlaced LC branches, including engineering customization, to match the network ports of electronic devices, so as to provide seamless integration between wiring infrastructure and electronic devices.
What is the typical application of the MTP-LC branch jumper line?
The MTP-LC branch jumper is used to copy the ports of the blade switch board to facilitate these ports to be connected to other devices. Based on specific applications and what components are inserted, it is divided into two types of branch jumpers, module branch jumpers and trunk branch jumpers.
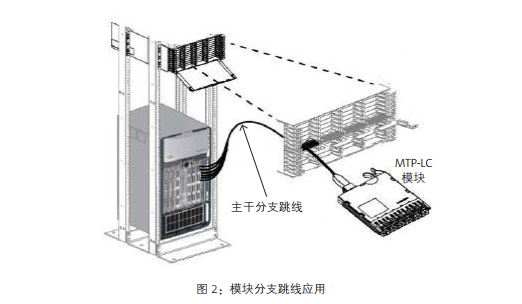
The module branch jumper is directly connected to the back of the MTP-LC module, and the switch port is copied to the rack in the same or adjacent frame. When this application is usually used, the switch is located on the MDA or the column header switching. Figure 2 describes an example of a module branch jump line application.
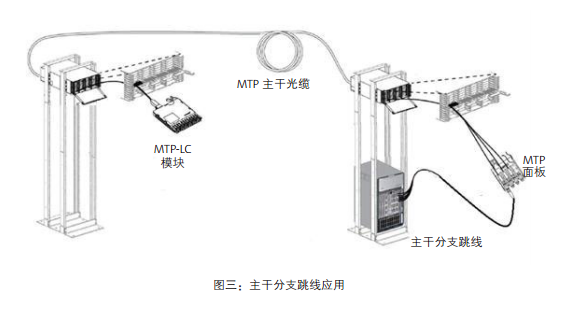
The switch mapped frame is located outside the location of the switch. Deploying this application is usually when you have a major distribution area (MDA) needed for a universal switching area and port replication. Figure 3 describes an example of a trunk branch jump line application.
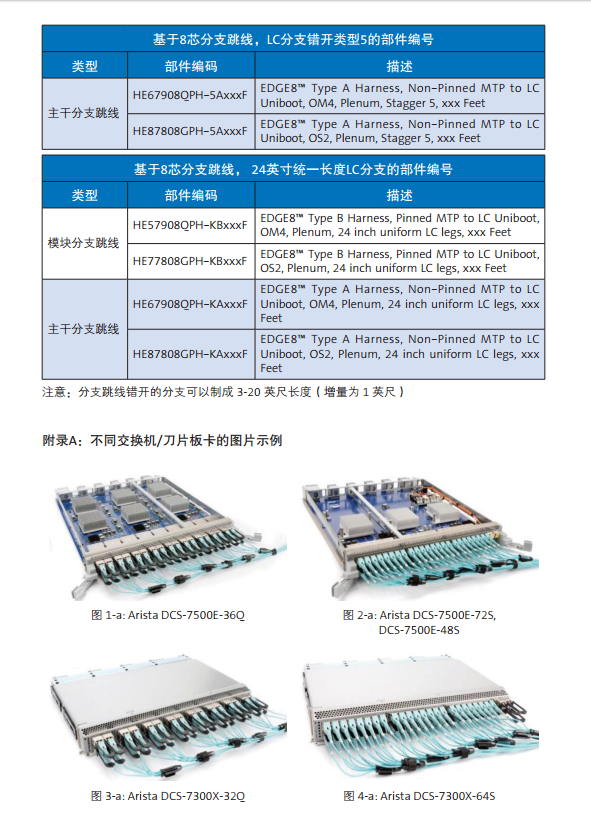
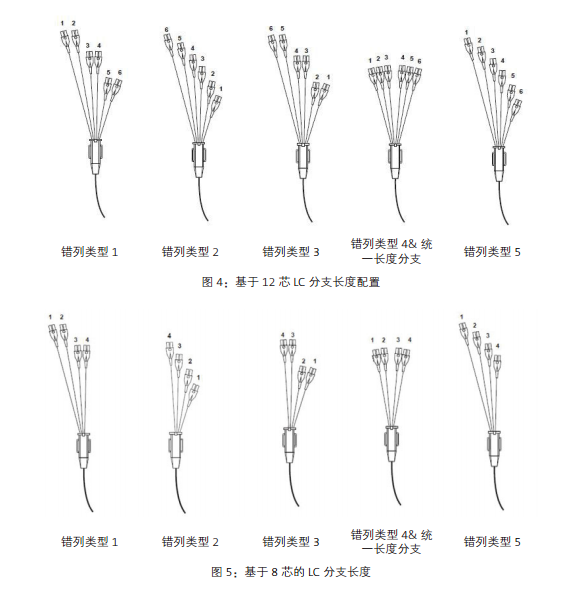
What kind of LC branch length should the MTP-LC branch jump line use?
The best branch jump line LC branch length will depend on the following factors: machine frame type, blade type, number of blade ports, port direction and routing routing. This paper provides customized, stagger branch branch jumpers for different industries to match every port of their data center switch series, providing seamless integration between wiring infrastructure and electronic devices.
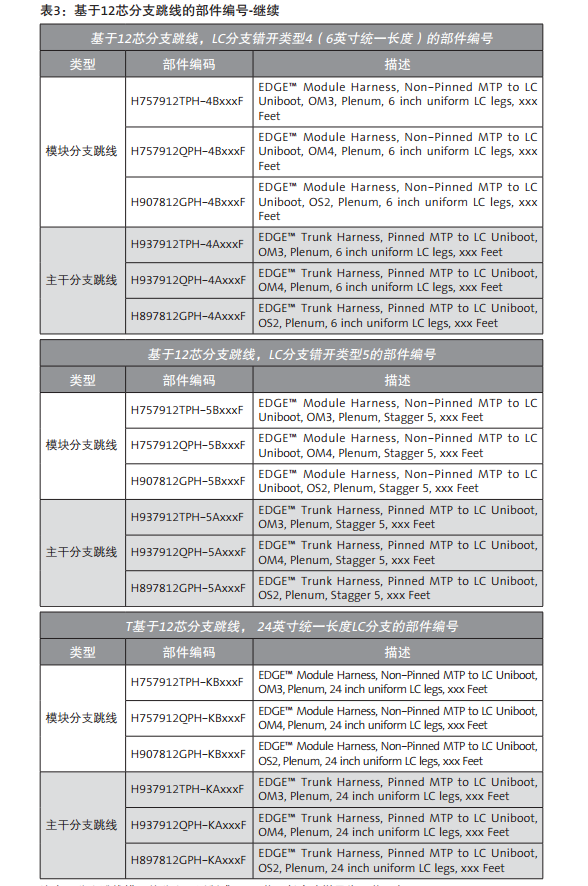
The wrong type 1, 2, 3, and 5 is the exact design length, which is specially matched to the switch ports of the different vendors. In addition, according to your wiring requirements, this paper provides various unified length / non stagger branch lengths (for example, 6 inches (stagger type 4 branches), 12 inches, 24 inches and 36 inches). Figures 4 and 5 show different misplaced types of configuration.
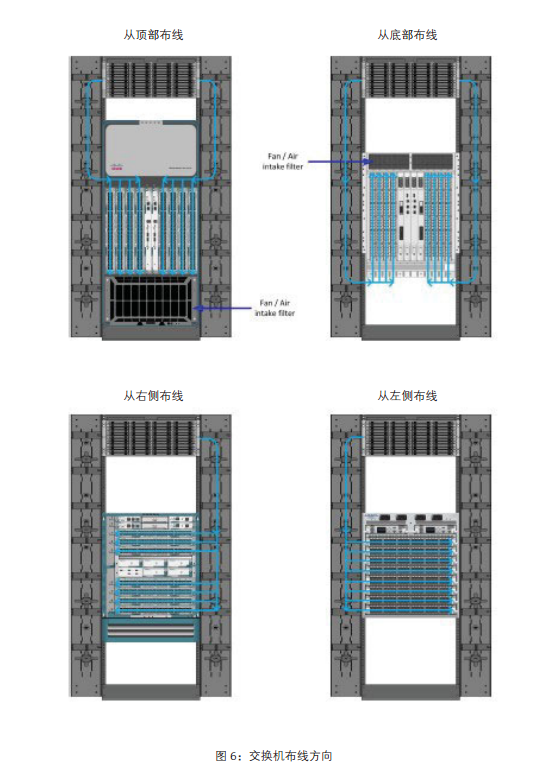
In which direction should the MTP-LC branch jump line be selected for the switch wiring?
The best switch direction will depend on two factors, the direction of the blade card and the fan / intake position. For example, if your switch is horizontal blade plate and fan / air intake position, it does not prevent branch jumpers from left or right, which can be attributed to customer preferences. On the other hand, if the fan / intake is on the side of the switch, you should put your branch jumper on the other side.
This is also suitable for the switch of the blade card in the vertical direction. This paper provides the optimal wiring direction for different industry manufacturers based on different switch machine frame products. Figure 6 shows the different wiring directions.
In which direction should the MTP-LC branch jump line be selected for the switch wiring?
The best switch direction will depend on two factors, the direction of the blade card and the fan / intake position. For example, if your switch is horizontal blade plate and fan / air intake position, it does not prevent branch jumpers from left or right, which can be attributed to customer preferences. On the other hand, if the fan / intake is on the side of the switch, you should put your branch jumper on the other side.
This is also suitable for the switch of the blade card in the vertical direction. This paper provides the optimal wiring direction for different industry manufacturers based on different switch machine frame products. Figure 6 shows the different wiring directions.
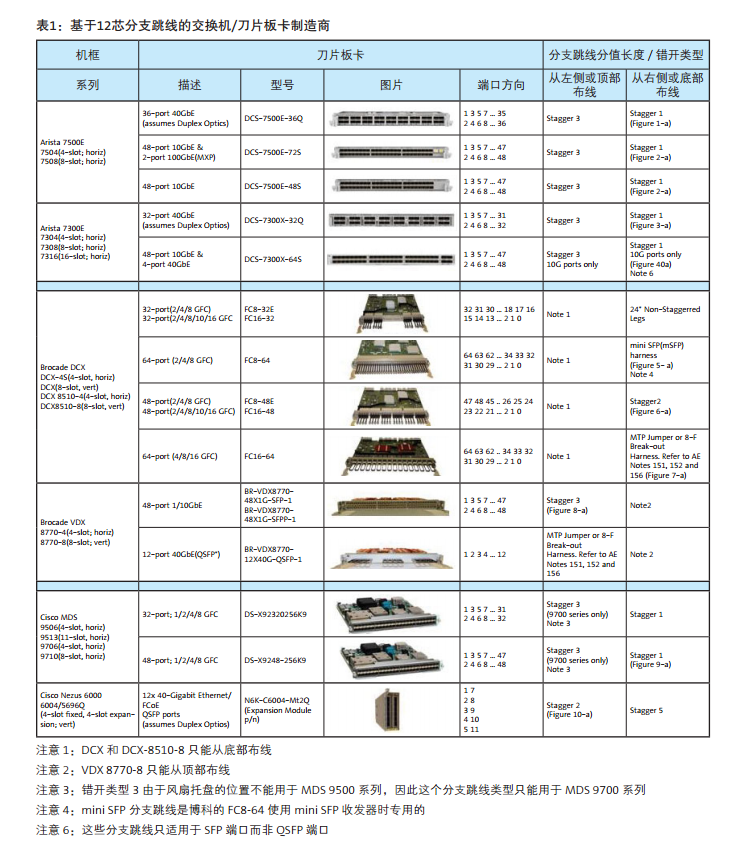
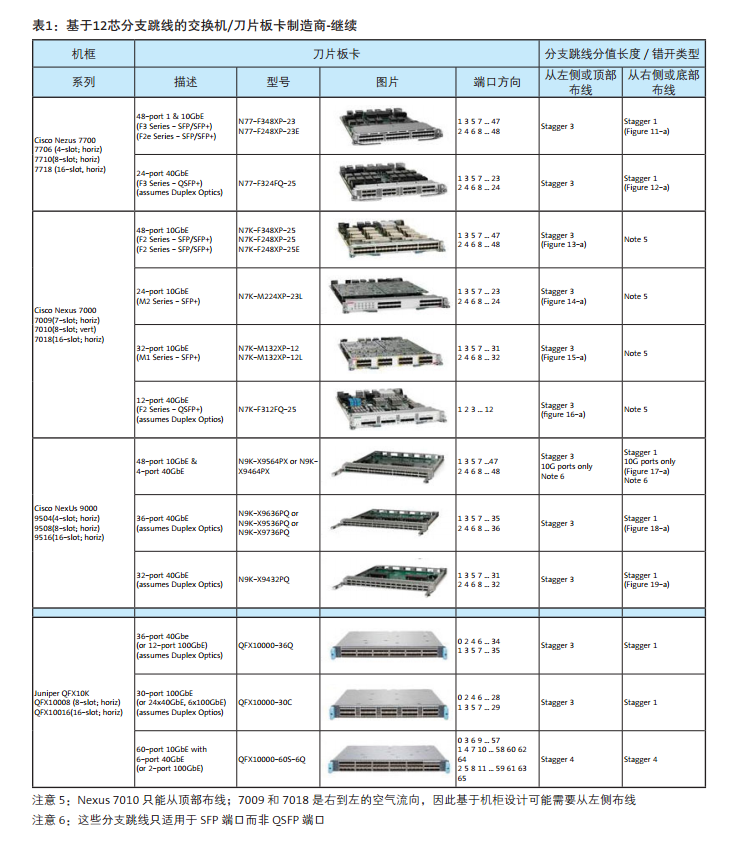
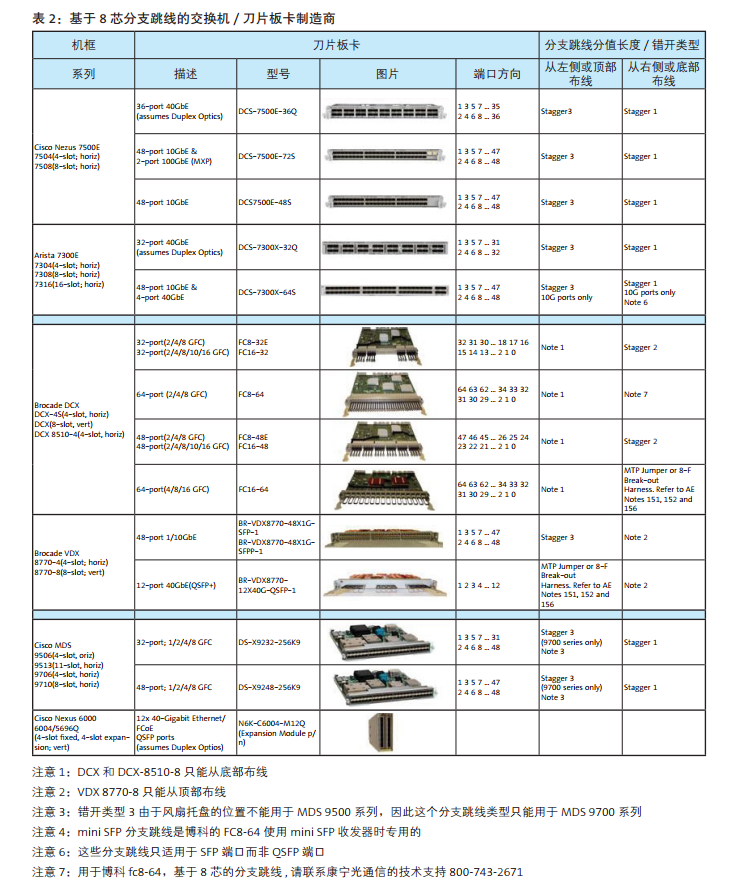
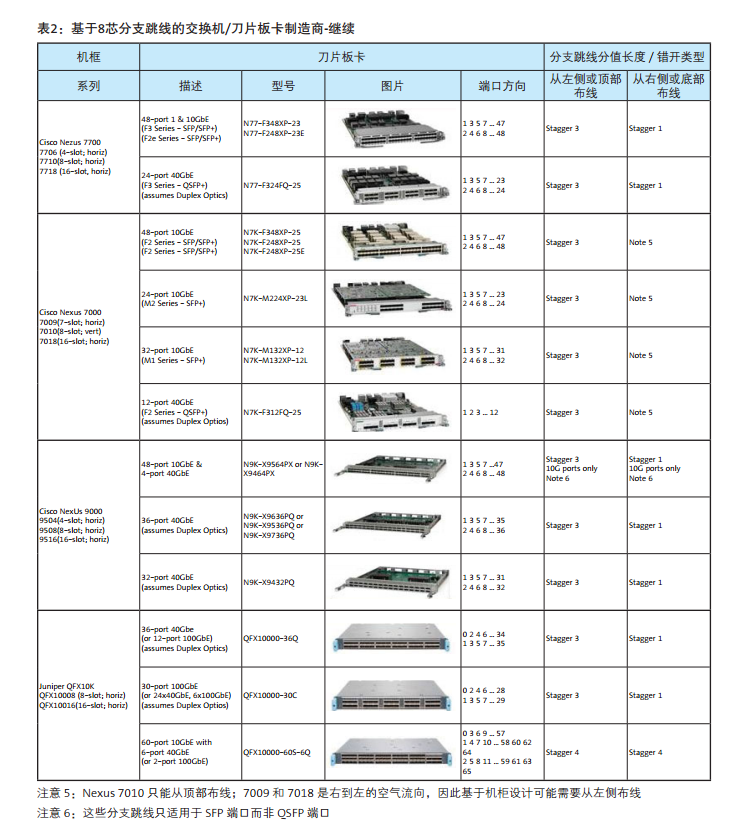
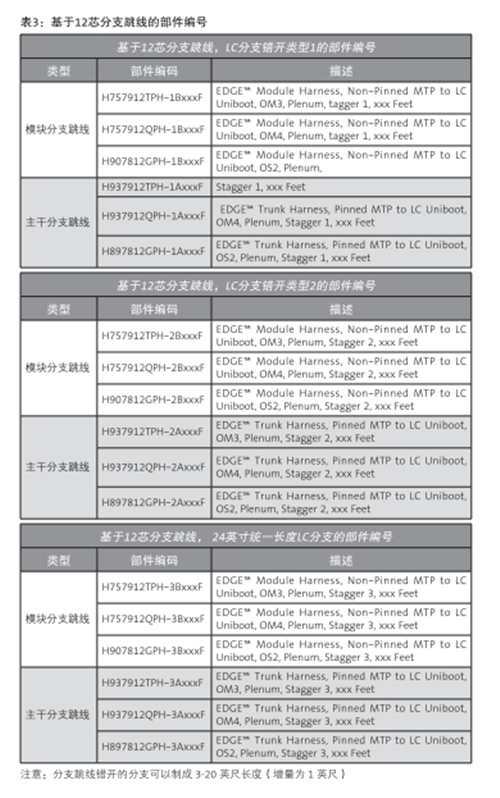
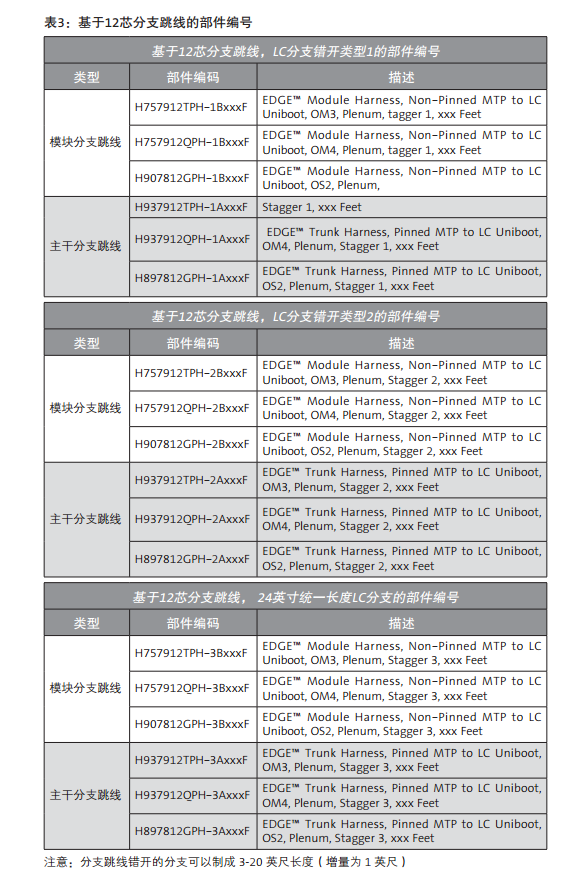
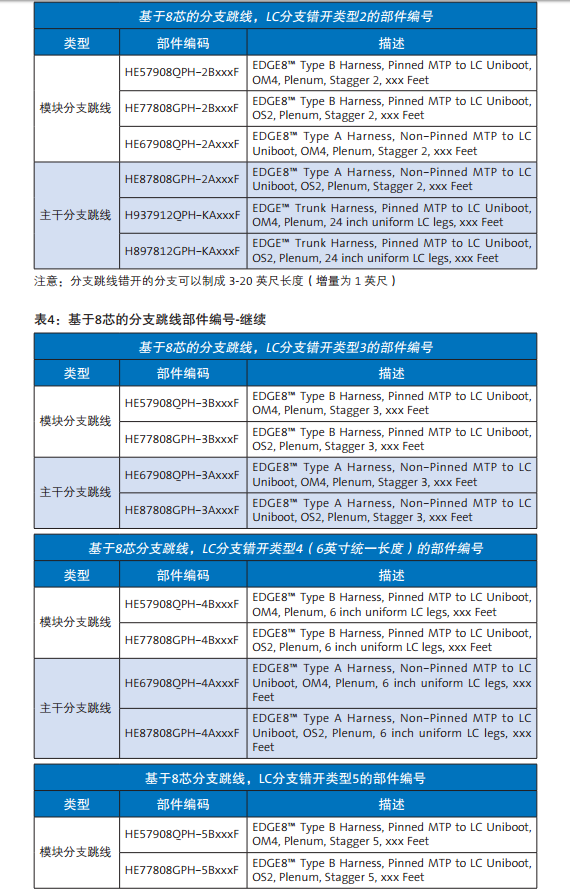
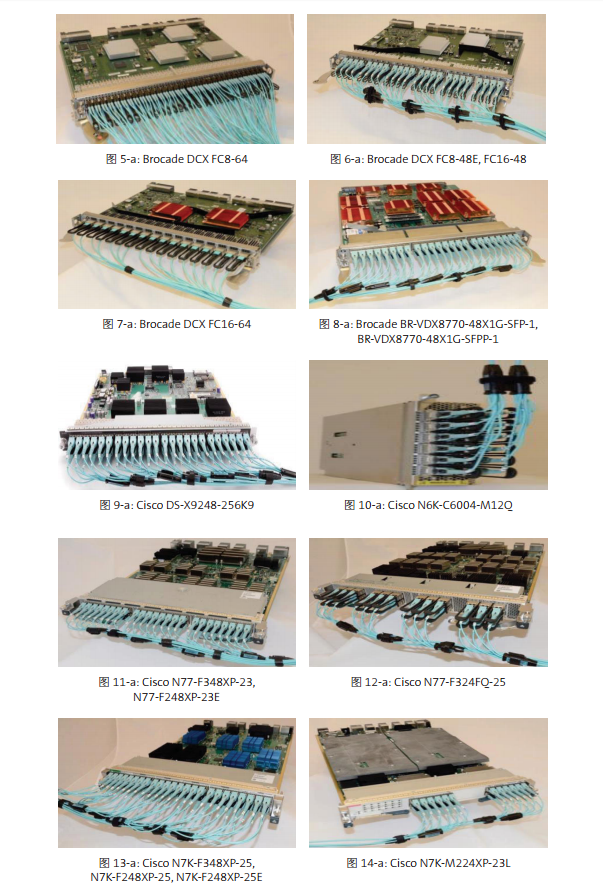
With the wide supply of switches in the network market, there are several configuration of MTP-LC branch jumpers to choose from. The rest of the information in this document will help you determine which branch jumpers are most suitable for storage networks or LAN switches wiring. On the next page is table 1 and table 2, summarize the use of 12 core or 8 core based branch jumpers, according to switch manufacturers, modules, ports number, port direction and wiring direction. The parts for each different branch line type are numbered in Table 3 and table 4. The illustrated example is the document that the MTP-LC branch jumper installed by a different switch / blade can be found in Appendix A.